AstroVision Model for Imaging and Spectroscopy (AVIS)
Designing a foundation model for astronomical imaging and spectroscopy
Abstract
Astronomical datasets have expanded dramatically in size and complexity over the past two decades, offering vast opportunities for exploration but posing challenges due to limited labeled data. Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) is an innovative technique to address this issue. We present some preliminary results from designing a foundation model – Astro Vision model for Imaging and Spectroscopy (AVIS) that can combine the information from imaging and spectroscopy. Our model is trained using DESI Y3 spectra and Legacy Imaging Survey (LS) DR9 and DR10 imaging data. Our analysis of embedding vectors generated by the trained model in latent space shows the model can understand the correlational features between images and spectra for each type of source (QSO, galaxies, stars, etc.). The model can perform redshift estimation without any supervisory information provided. We will examine these diagnostics and discuss some further analysis on the model to evaluate its understanding of astrophysical objects. Some potential downstream science applications will also be considered.
Clustering analysis of embedding vectors
We perform clustering analysis on the embedding vectors generated by the AVIS model for DESI Y3 sources. We use the Pairwise Controlled Manifold Approximation (PaCMAP) algorithm to reduce the high-dimensional embedding vectors into 2D and 3D spaces for visualization. The clusters are clearly separated with various meaning. In the following figures, we color the points based on different properties of DESI sources to understand the clustering results.
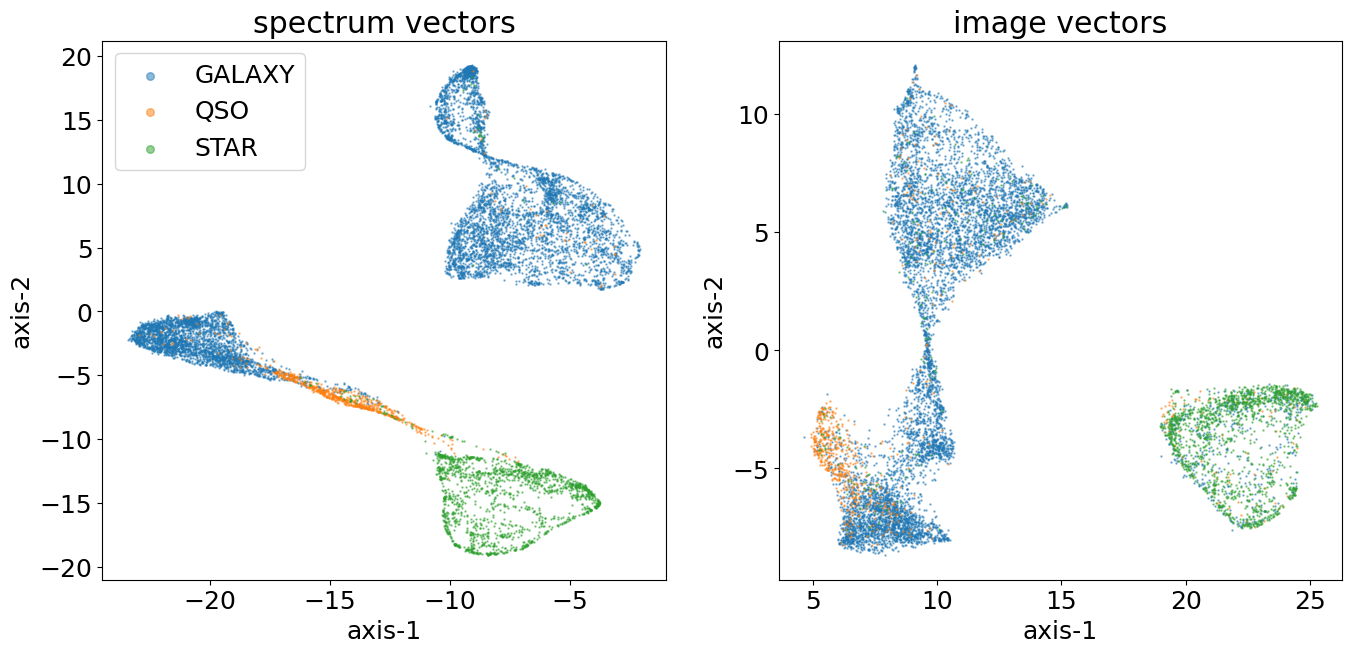
Clustering results with SPECTYPE
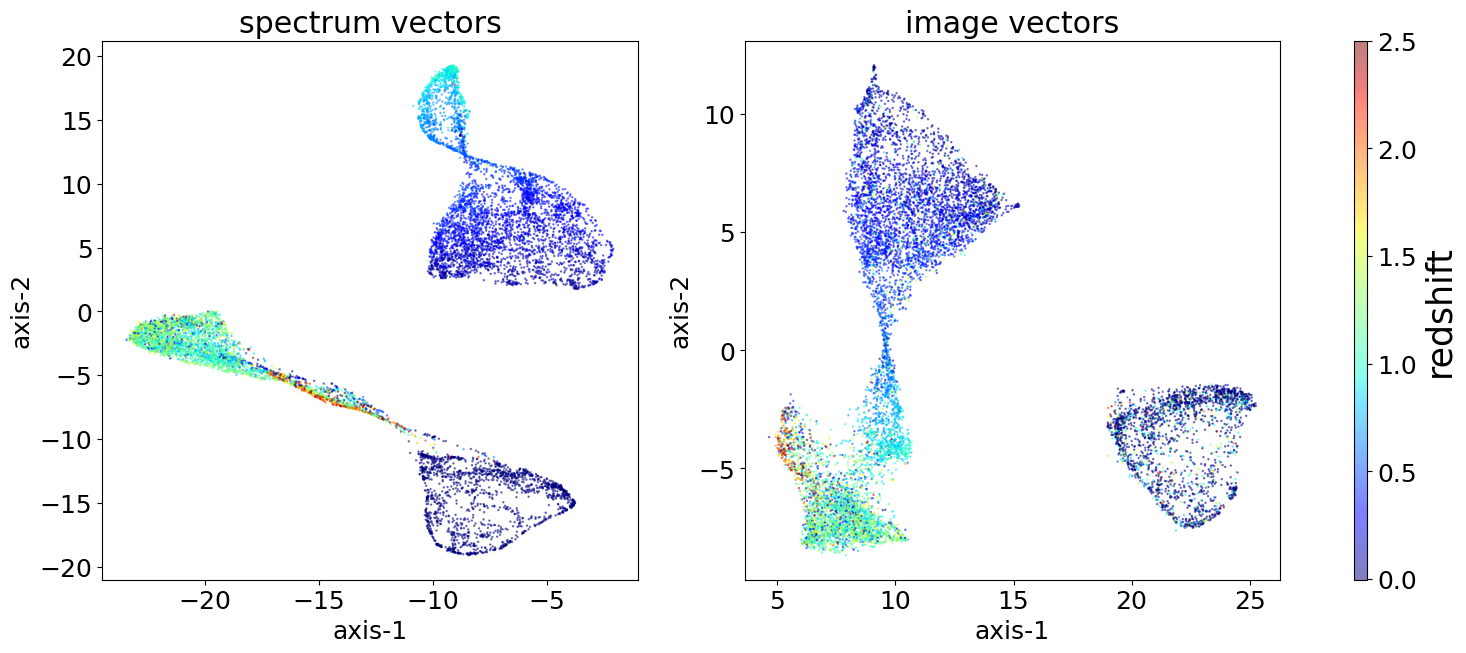
Clustering results with redshift
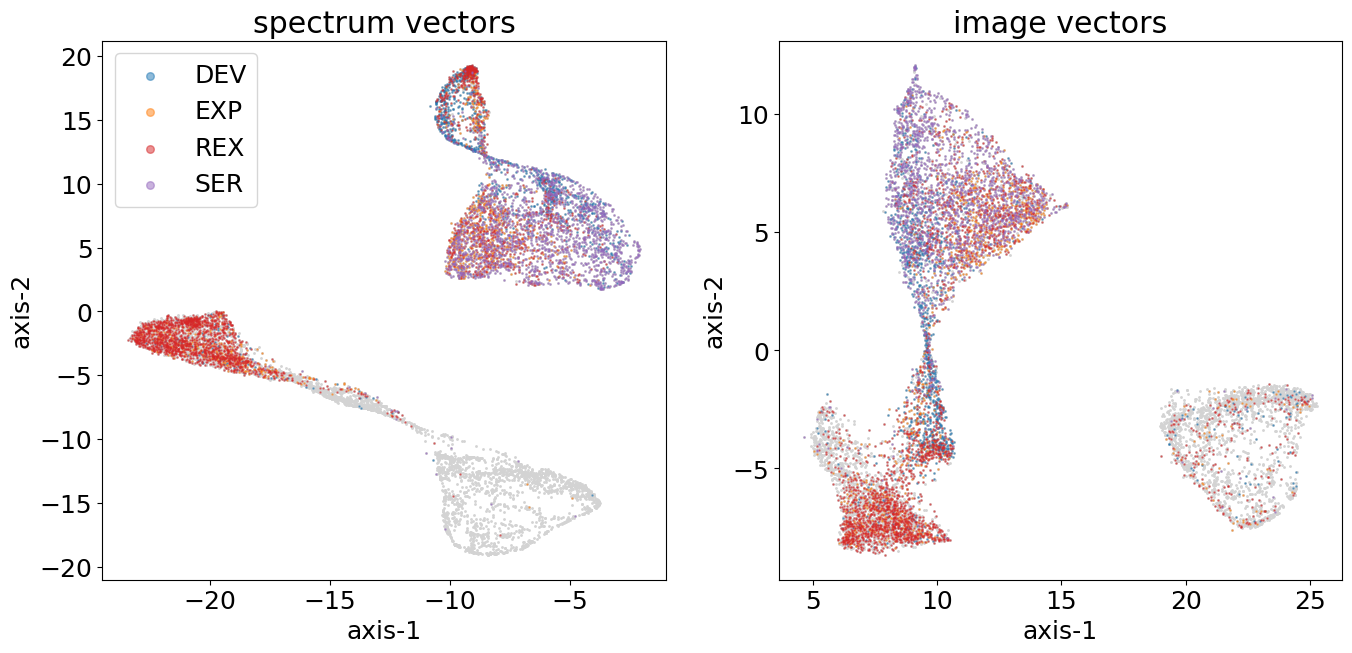
By morphological types
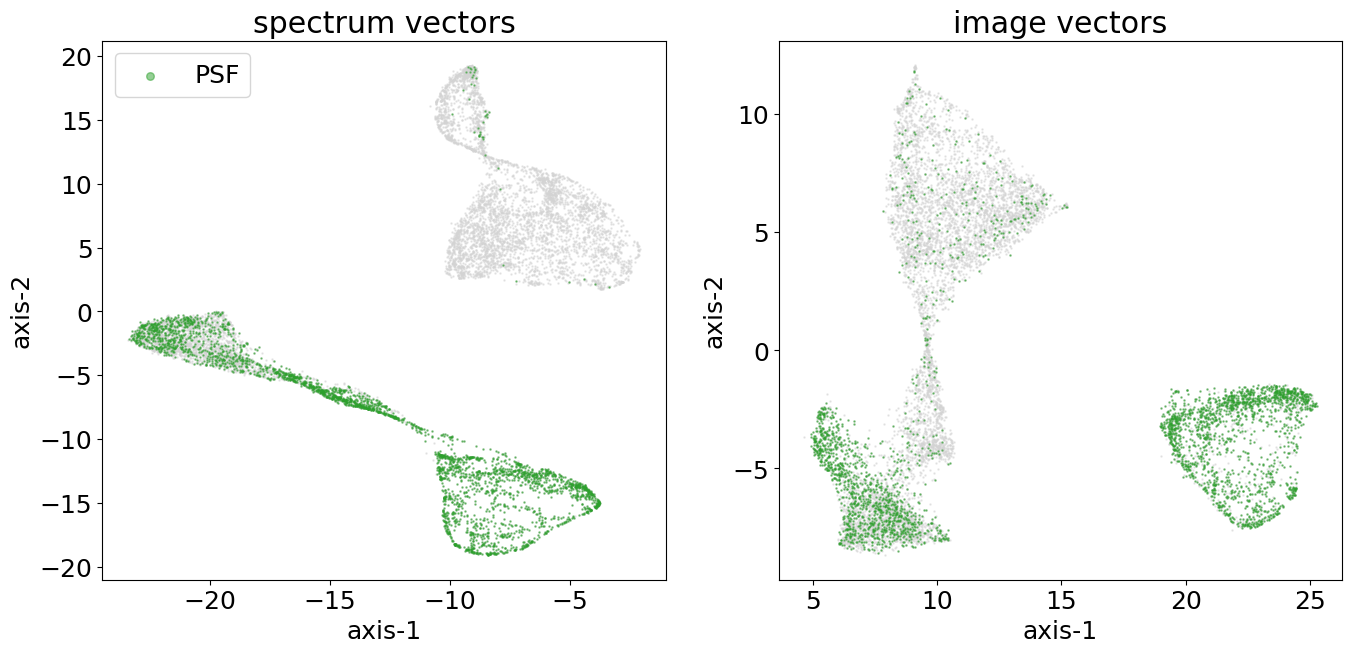
By half-light radius
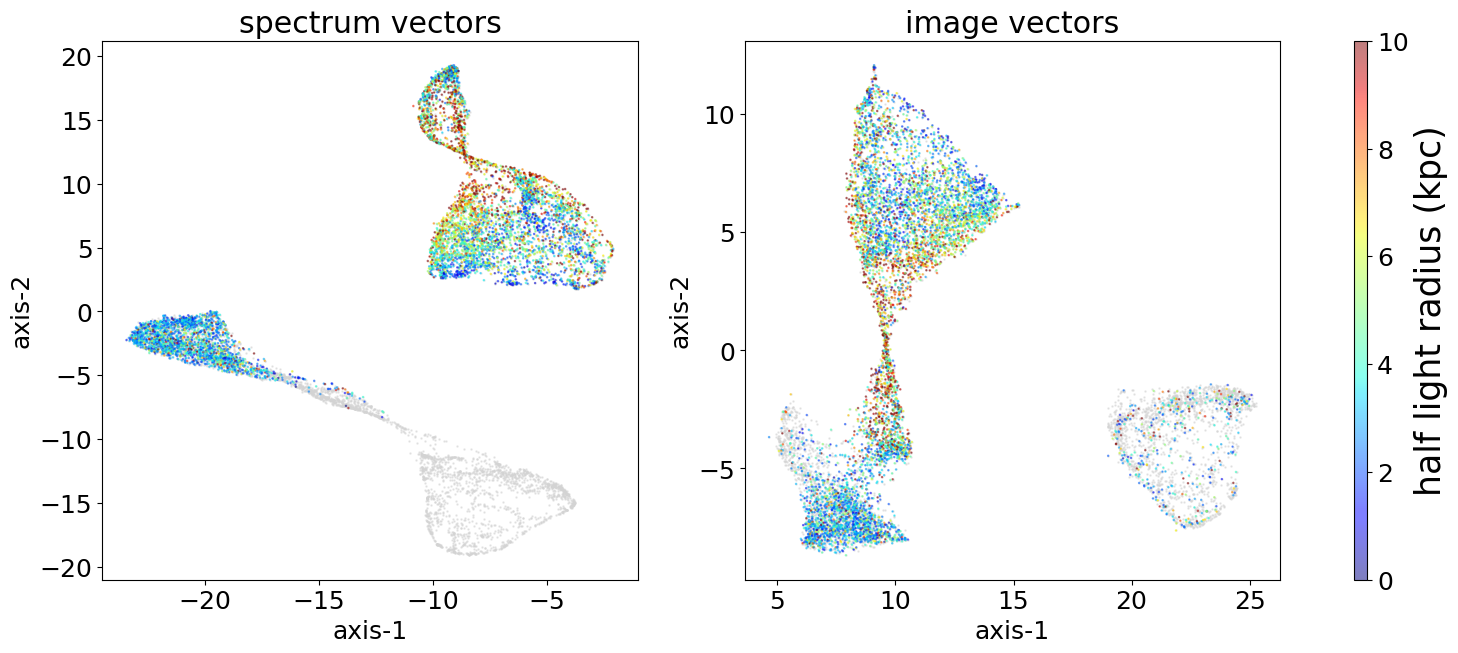
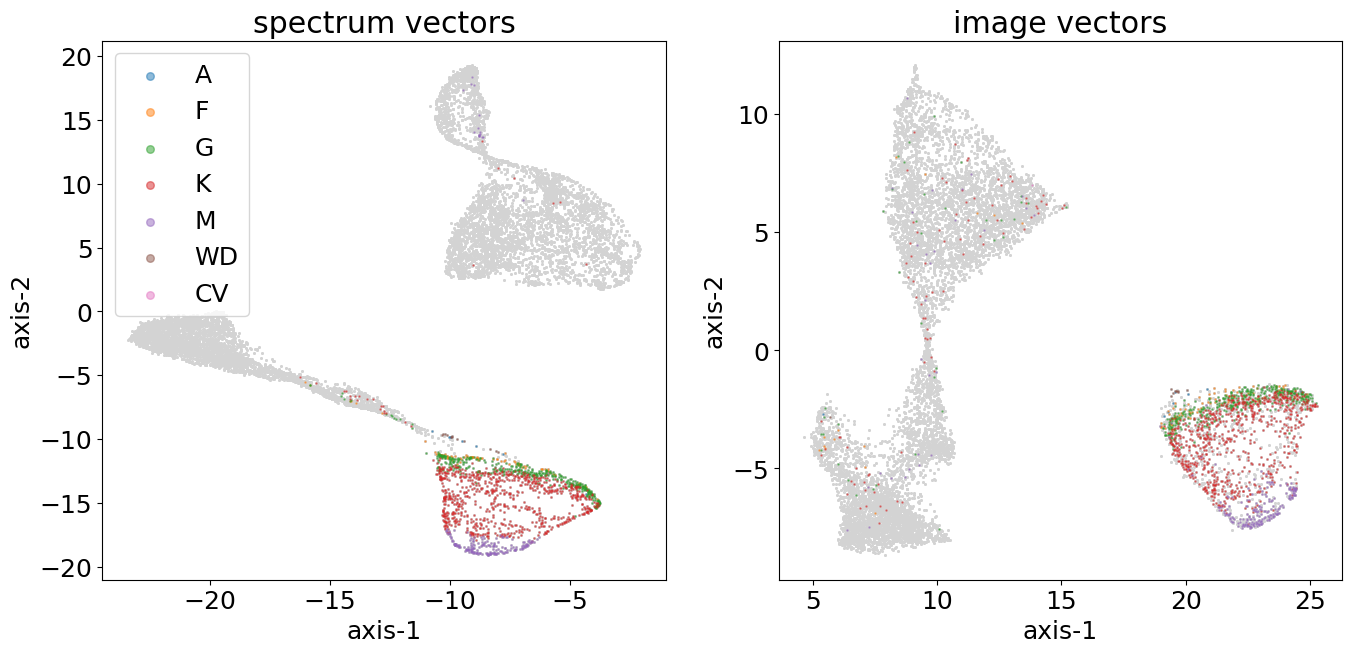
By stellar
Sources are classified via spectral fitting into different stellar subtypes (A, F, G, K, M, WD, CV).
Clustering results with DESI Target classes
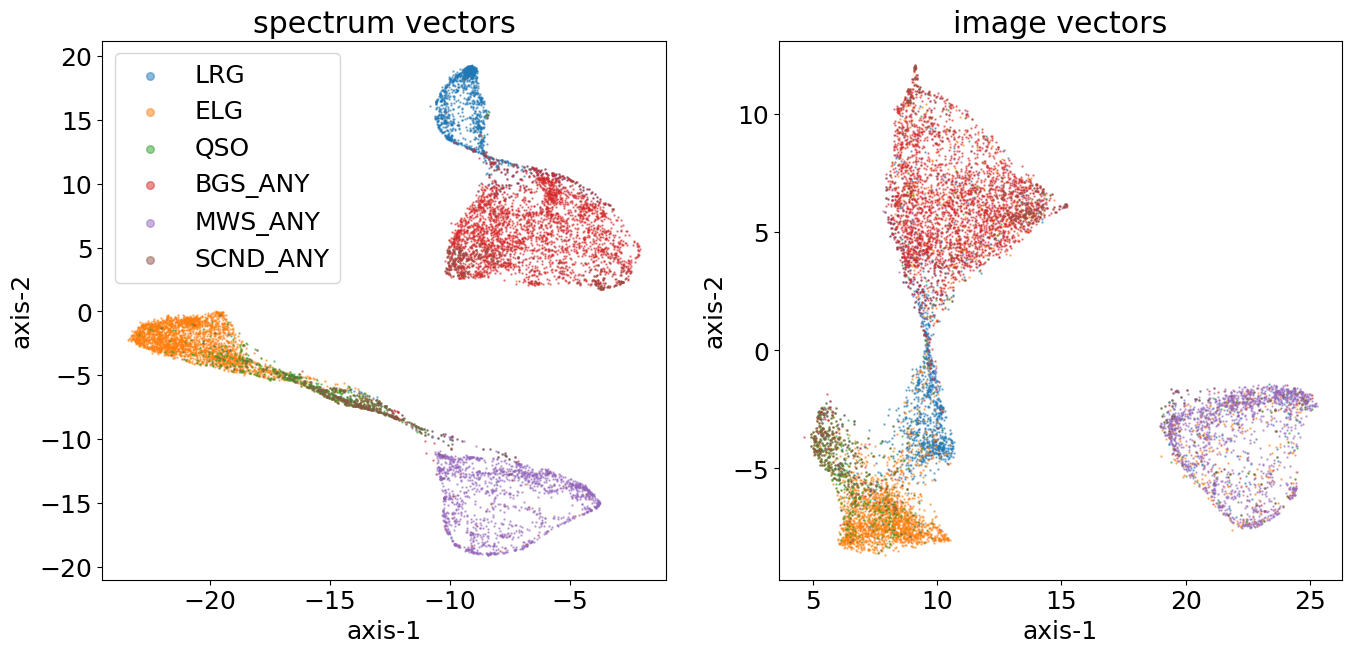
The 3D interactive plot for clustering results with DESI Target classes
Click on this link to access the full interactive plot: Interactive Plot
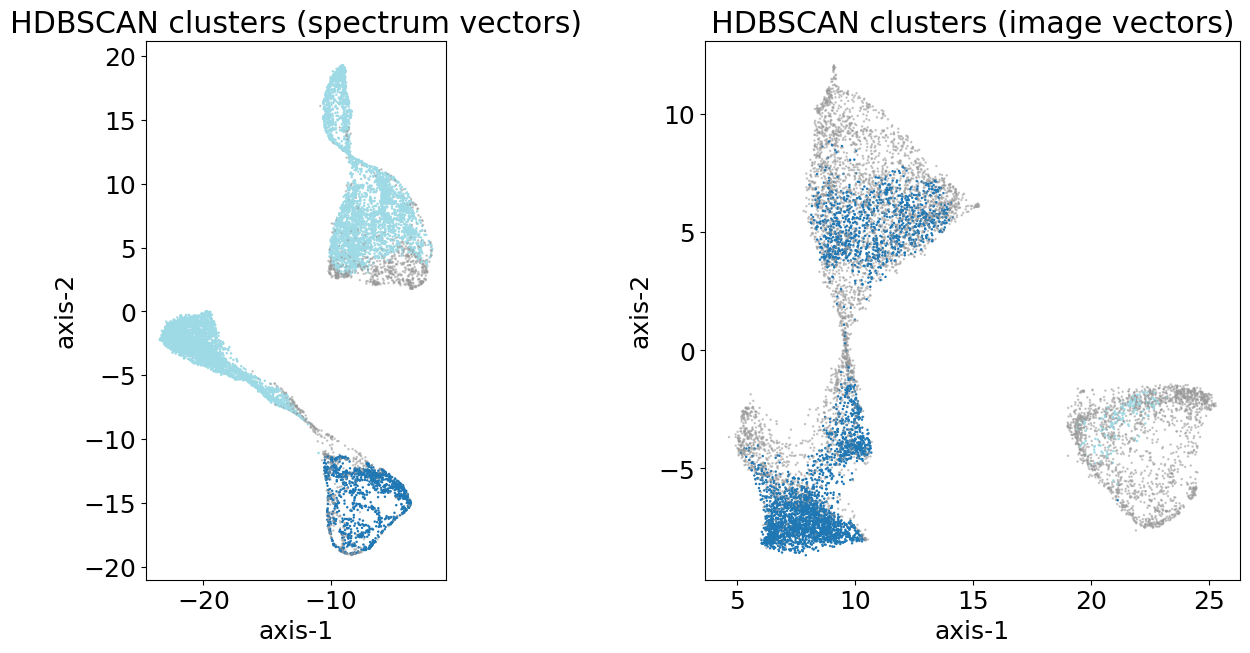
Self clustering
We also perform self-clustering on the embedding vectors without any labels. We use the HDBSCAN algorithm to identify clusters in the embedding space. The results show that the model can group similar sources together based on their learned features.